Knowing the language of target audience when creating ad campaign is essential (as much as high quality traffic source), but understanding how and where those languages are used is even better. Here are top five reasons why you must consider this advertising strategy for your next ad campaign:
Wider Reach
Targeting the second most spoken language expands your audience within multilingual regions, increasing ad exposure.
Higher Engagement
When ads are displayed in a language familiar to users, it enhances their engagement and boosts conversions by reducing possible language barriers.
Cost-Effectiveness
While major part of advertisers focus on targeting first-used languages, you can optimize your ad budget by working with the second language usen on this GEO. Such a strategy will lead you to a lower ad costs.
Localized Experience
Ads in regional second languages provide a personalized touch, fostering trust and stronger brand connections with local audiences.
Now, as you know the value of the multilingual targeting, let’s go on with the insights about popularity of different languages in not expected regions.
How Browser Language Is Defined
Before we jump to results of our Research, let’s briefly explain to you how browser languages are defined within our experiments.
The technical backbone of this research lies in the HTTP protocol, which facilitates the exchange of information between a user’s device and a server. Included in this exchange are special headers, one of which is the Accept-Language header. This type of header contains data about the user’s browser language preferences, often used by multilingual websites to display the most suitable version for the user.
Here’s an example of an Accept-Language header:
Accept-Language: fr-CH, fr;q=0.9, en;q=0.8, de;q=0.7, *;q=0.5
In this example, languages are listed in order of preference, with tags like “fr-CH” representing the French language used in Switzerland.
To ensure accuracy of provided data, we analyzed all languages mentioned in tags across various GEOs.
Multilingual Map: Popular Languages Across Regions
Our research revealed a fascinating landscape of linguistic diversity. The map below highlights countries where two languages are prevalent versus those where three or more languages are commonly used.
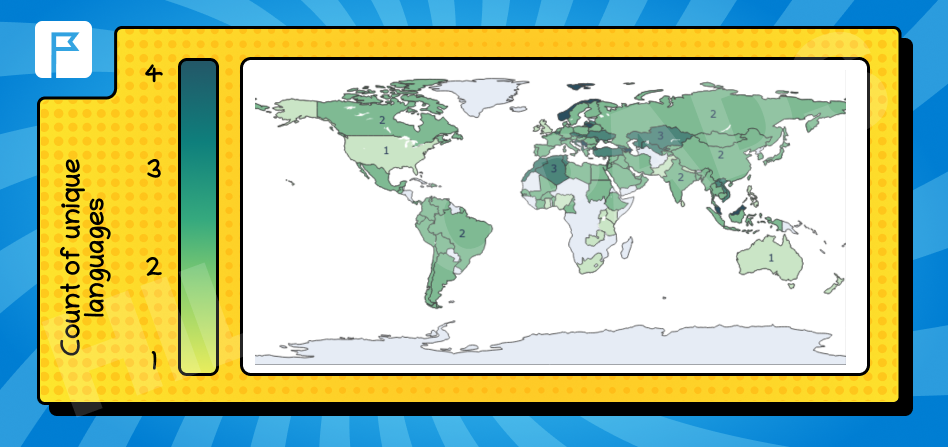
For our analysis, we considered a language “often used” in a GEO if at least 10% of users had it set as their browser language.
The majority of countries predominantly use two languages: their native language and English. However, some GEOs showed a variety, with three or even four languages in use. On the other hand, in English-speaking regions, alternative languages were seldom used.
Regions with Linguistic Diversity
To better understand linguistic diversity, we excluded English from our analysis. The chart below shows countries where three or more languages are commonly used:
This subset highlights GEOs with significant multilingual populations, underscoring the importance of tailoring campaigns to these diverse audiences.
Top Second Languages
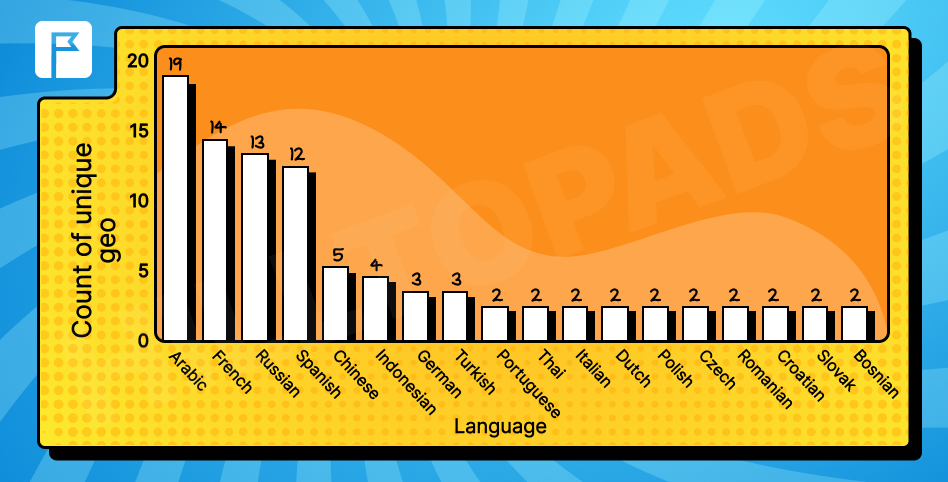
When examining second languages–excluding English–our findings identified eight languages that are widely used in three or more countries:
- Arabic: Used in 19 GEOs
- French: 14 GEOs
- Russian: 13 GEOs
- Spanish: 12 GEOs
- Chinese: 5 GEOs
- Indonesian: 4 GEOs
Let’s take a closer look at the geographical distribution and factors influencing the popularity of each language.
Each map from below provides a detailed overview of where widely spoken languages are used around the world:
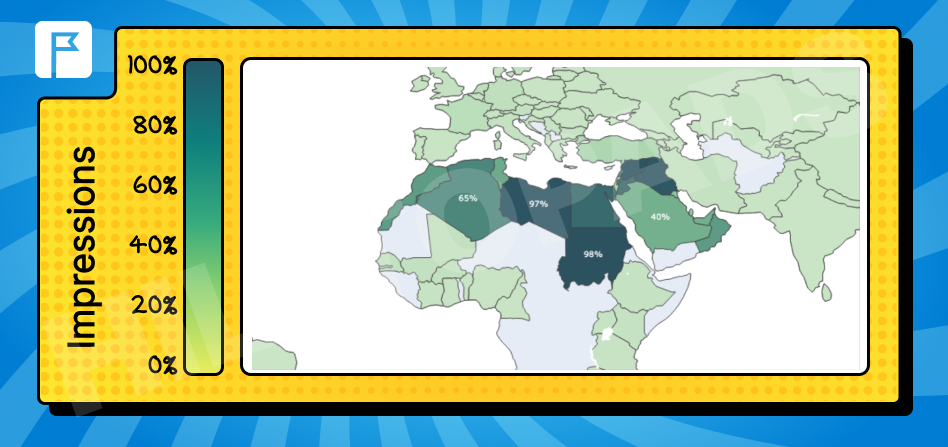
Arabic
Predominantly in North African countries and Southwest Asia.
French
In France and several countries in Northwest Africa.
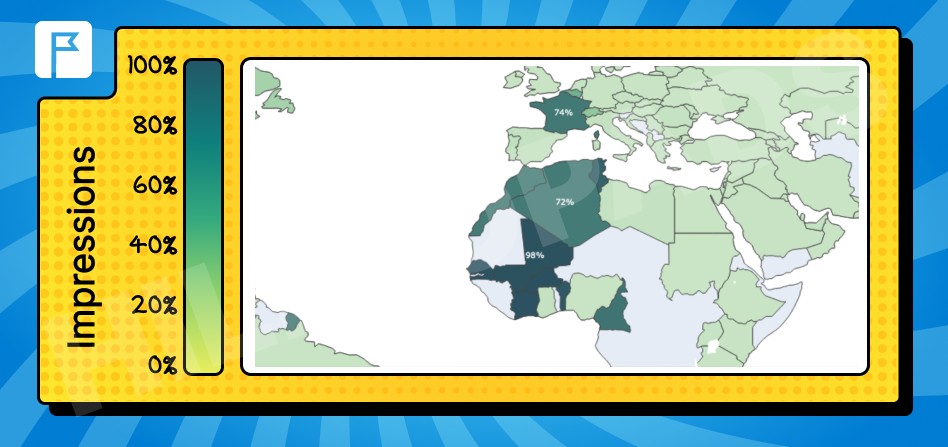
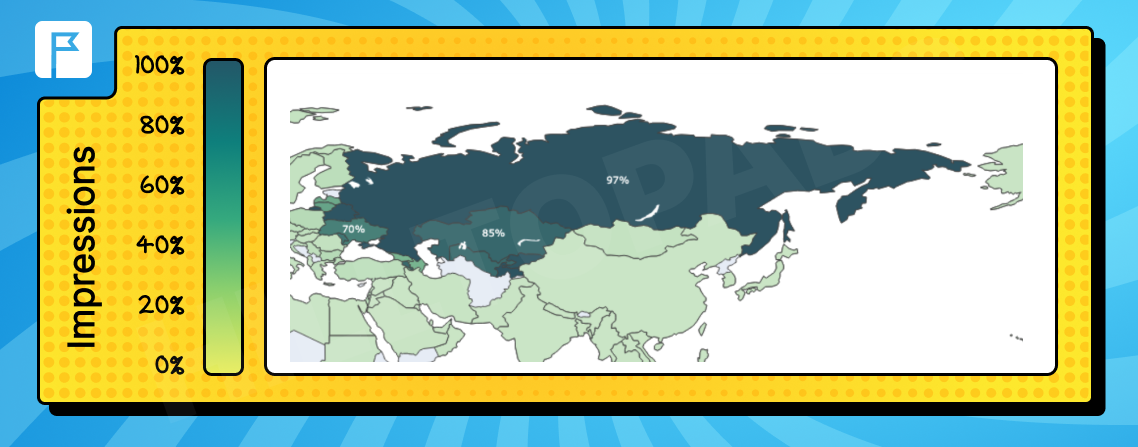
Russian
Spoken in Russia, Central Asian countries, and Eastern Europe.
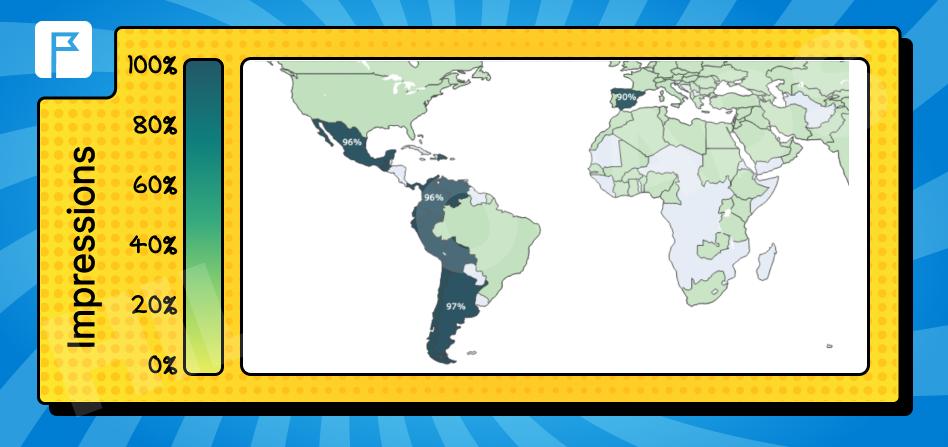
Spanish
Found in Spain, Mexico, and South America.
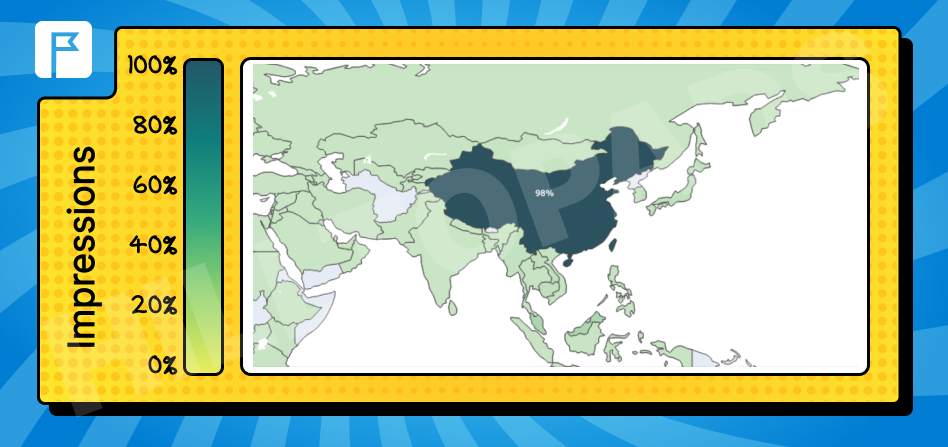
Chinese
Primarily in China and some Southeast Asian countries.
Indonesian
Commonly used in Southeast Asian countries.
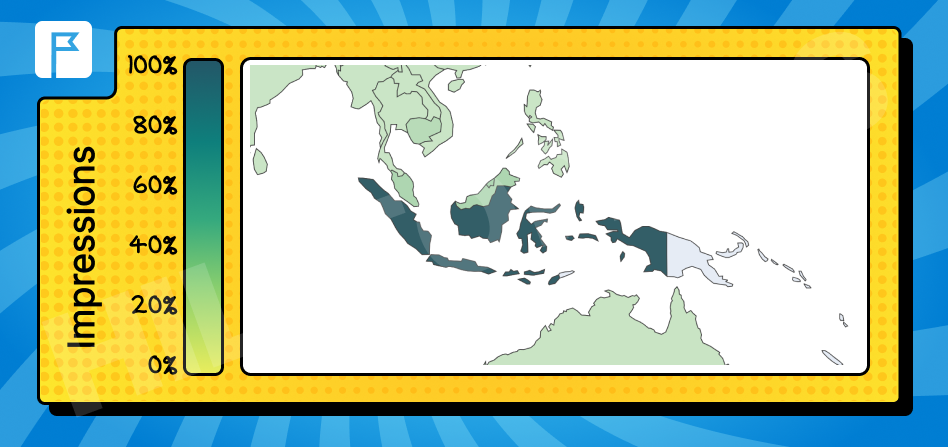
Fluctuations in Data When Counting Only the First Language
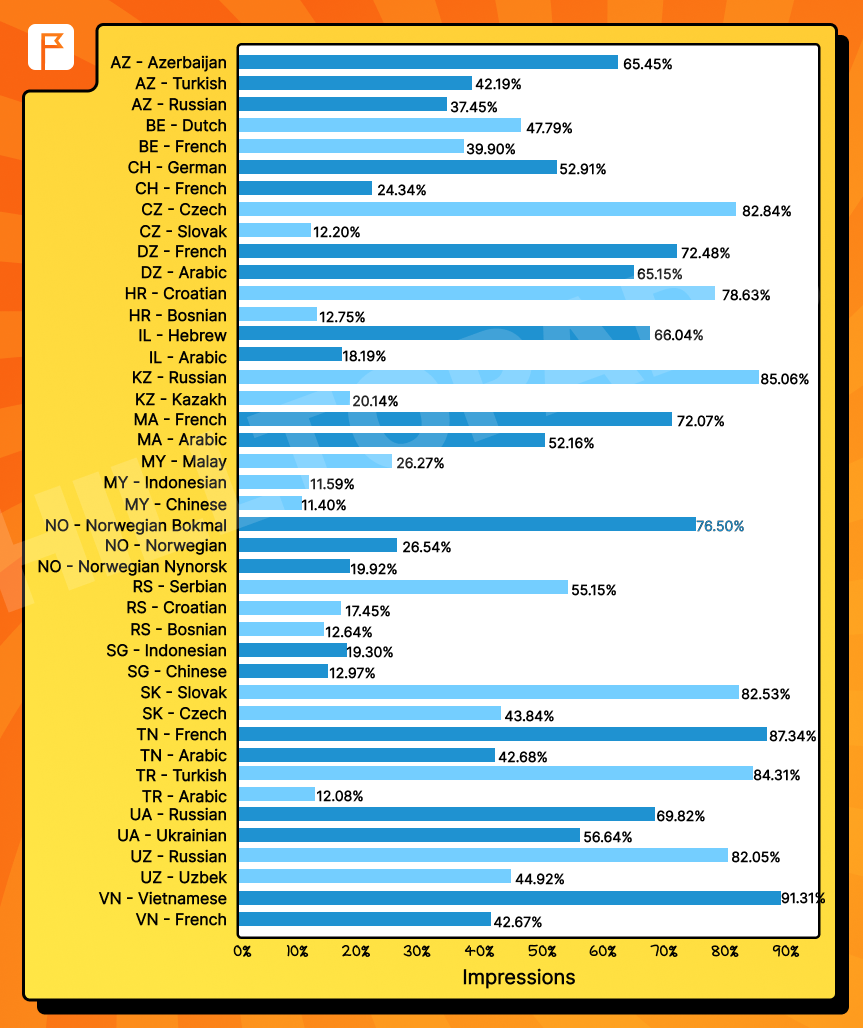
Interestingly, we noticed discrepancies when analyzing only the first-listed language in the Accept-Language header. In some cases, widely spoken languages were not prioritized, highlighting the need for a nuanced approach to targeting.
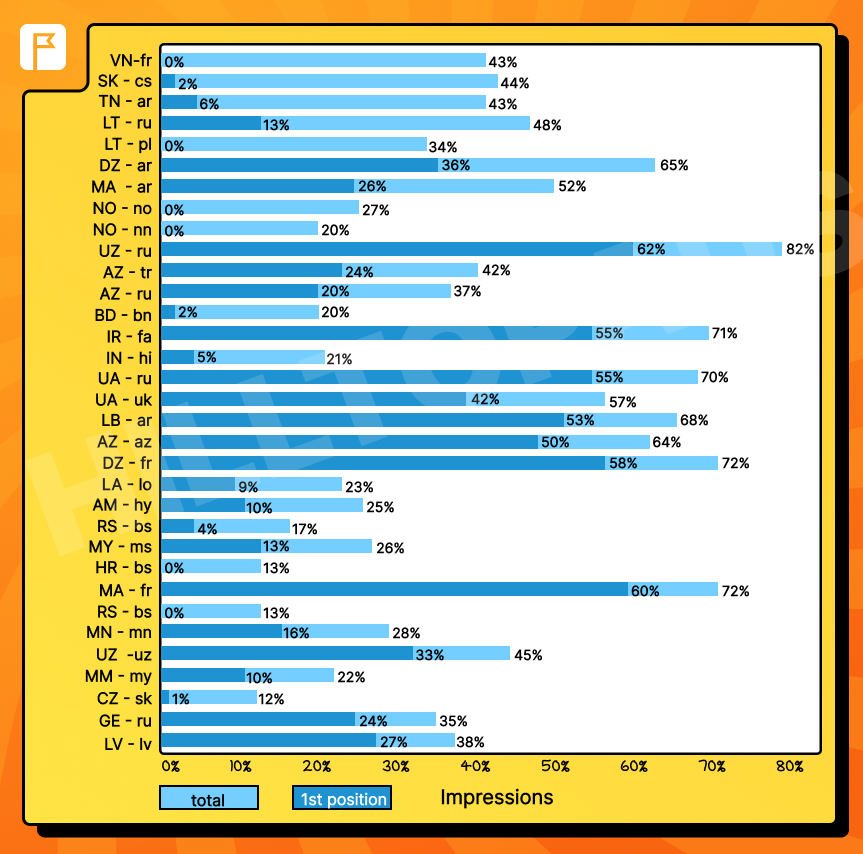
This graph shows GEO-language pairs where significant deviations occurred between the most commonly used language and the one that listed first in the header. Such fluctuations reflect the importance of accounting for all possible languages rather than relying solely on the first one.
Smart language targeting also plays a key role in promoting vpn offers, when user’s online geolocation doesn’t match the actual location.
Final Thoughts
Aside from English, which remains a universal language for all of digital communication, six more languages–Arabic, French, Russian, Spanish, Chinese, and Indonesian–stand out for their regional significance. Including these languages in your targeting settings can significantly enhance campaign reach and effectiveness.
Most countries primarily use their native language alongside English, but overlooking additional widely spoken languages can lead to missed opportunities. This is why we recommend you to complete a pre-analysis of target GEO, and leverage its full potential with HilltopAds’ advanced targeting capabilities to maximize your campaign’s potential.
Ready to put your new knowledge into practice? Click the button to create an ad campaign with HilltopAds ad network!


















