If you find the subject of this article intriguing, you’re probably either a newcomer with no prior knowledge of affiliate marketing, or an expert who has missed this particular detail and has hesitated to inquire about it with peers. Regardless of your experience level, you’re in the right place, as this article will guide you through the key distinctions between advertising and affiliate networks, along with revealing tips for maximizing their use in your digital marketing toolkit. Let’s begin with the fundamentals.
Advertising networks explained
Advertising networks are crucial for any marketer aiming to enhance their online presence and drive sales. An ad network serves as a bridge connecting advertisers with websites that wish to host advertisements, functioning as an intermediary that aggregates ad space supply from publishers and matches it with advertiser demand. This system allows for the efficient distribution of advertisements across a wide array of online platforms, ensuring that advertisers can reach their target audience more effectively, while publishers monetize their content.
How does the advertising network operate?
Ad Networks streamline the ad placement process by:
- Aggregating available ad spaces from publishers;
- Matching these spaces with advertisers’ needs, based on criteria like target audience demographics or behaviors;
- Utilizing programmatic advertising for automated decision-making, ensuring ads are placed where they can achieve the highest engagement and conversion rates.
Types of advertising networks
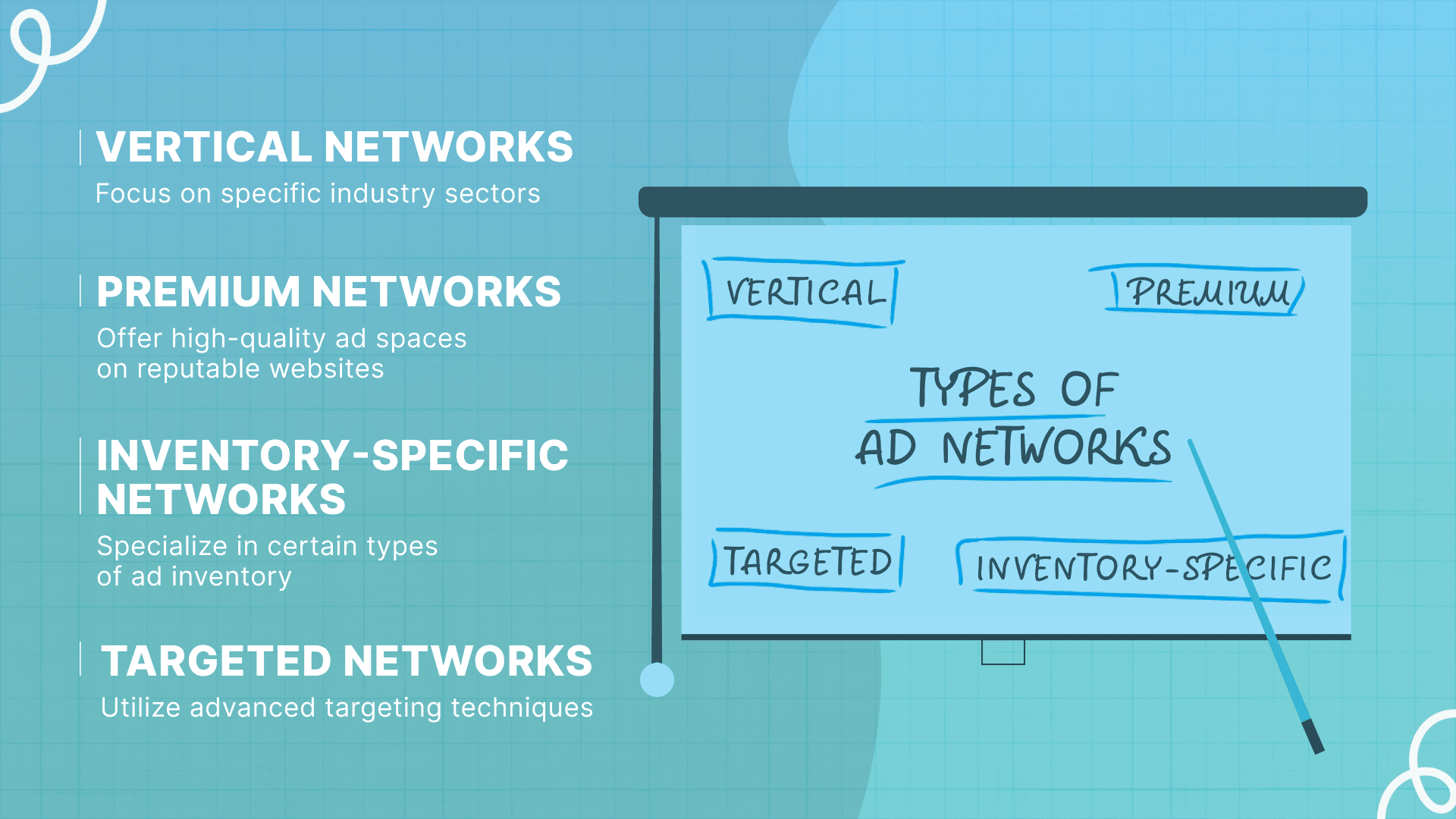
There are several varieties of ad networks, each designed to meet different advertising objectives:
- Vertical networks
Focus on specific industry sectors, connecting advertisers with publishers in niche markets for more relevant ad placements. These networks cater to particular interests or industries, offering targeted reach and engagement within a defined sector. - Premium networks
Offer high-quality ad spaces on reputable websites, typically attracting major brands willing to pay a premium for visibility on top-tier sites. These networks prioritize exclusive content and audiences, ensuring advertisers access to prime digital real estate. - Inventory-specific networks
Specialize in certain types of ad inventory, such as mobile, video, or banner ads, allowing advertisers to focus their efforts on the formats most effective for their campaigns. These networks provide a concentrated approach to ad format selection. - Targeted networks
Utilize advanced targeting techniques based on demographics, behaviors, or interests to connect advertisers with the most relevant audiences. These networks enhance campaign performance by focusing on precision and relevance in ad delivery.
Advantages of using ad networks
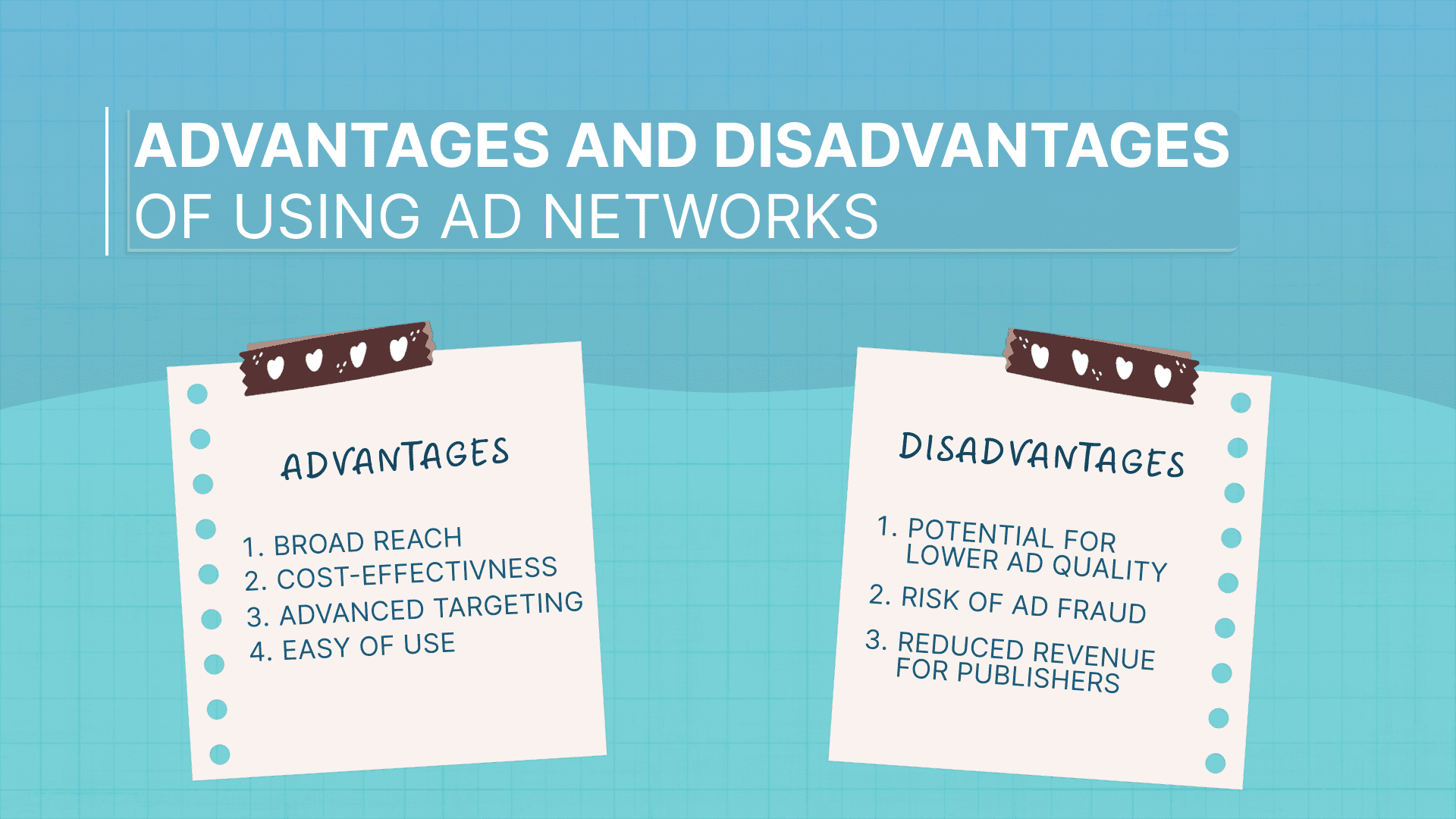
Utilizing ad networks offers multiple benefits, including:
- Broad reach: Access to a vast network of publishers.
- Cost-effectiveness: Efficient use of advertising budgets.
- Advanced targeting: Ability to reach specific audiences.
- Ease of use: Simplifies the ad buying process for advertisers.
Disadvantages of using ad networks
However, there are challenges to consider:
- Potential for lower ad quality: Broad targeting can sometimes lead to less relevant ad placements.
- Risk of ad fraud: Automated systems may be susceptible to fraudulent activities.
- Reduced revenue for publishers: Earnings may be lower compared to direct ad sales.
Affiliate networks explained
Affiliate networks act as a pivotal intermediary in the affiliate marketing ecosystem, bridging the gap between merchants (or advertisers) and affiliate marketers. Unlike an individual affiliate program that is managed directly by a merchant to promote its products or services, an affiliate network aggregates multiple affiliate programs under one platform, providing affiliates with a broad range of products and services to promote. This distinction allows affiliate marketers to access and manage campaigns for various merchants through a single interface, simplifying the process of finding and participating in affiliate marketing opportunities.
Affiliate marketing process through network
- Selection: Affiliates choose products or services from the network’s offerings to promote.
- Promotion: Affiliates use a unique tracking link provided by the network to promote the selected products or services through various channels such as blogs, social media, or email marketing.
- Tracking and earnings: The network tracks conversions generated through these links, attributing sales or actions to the respective affiliates and calculating their commissions accordingly.
Types of affiliate networks
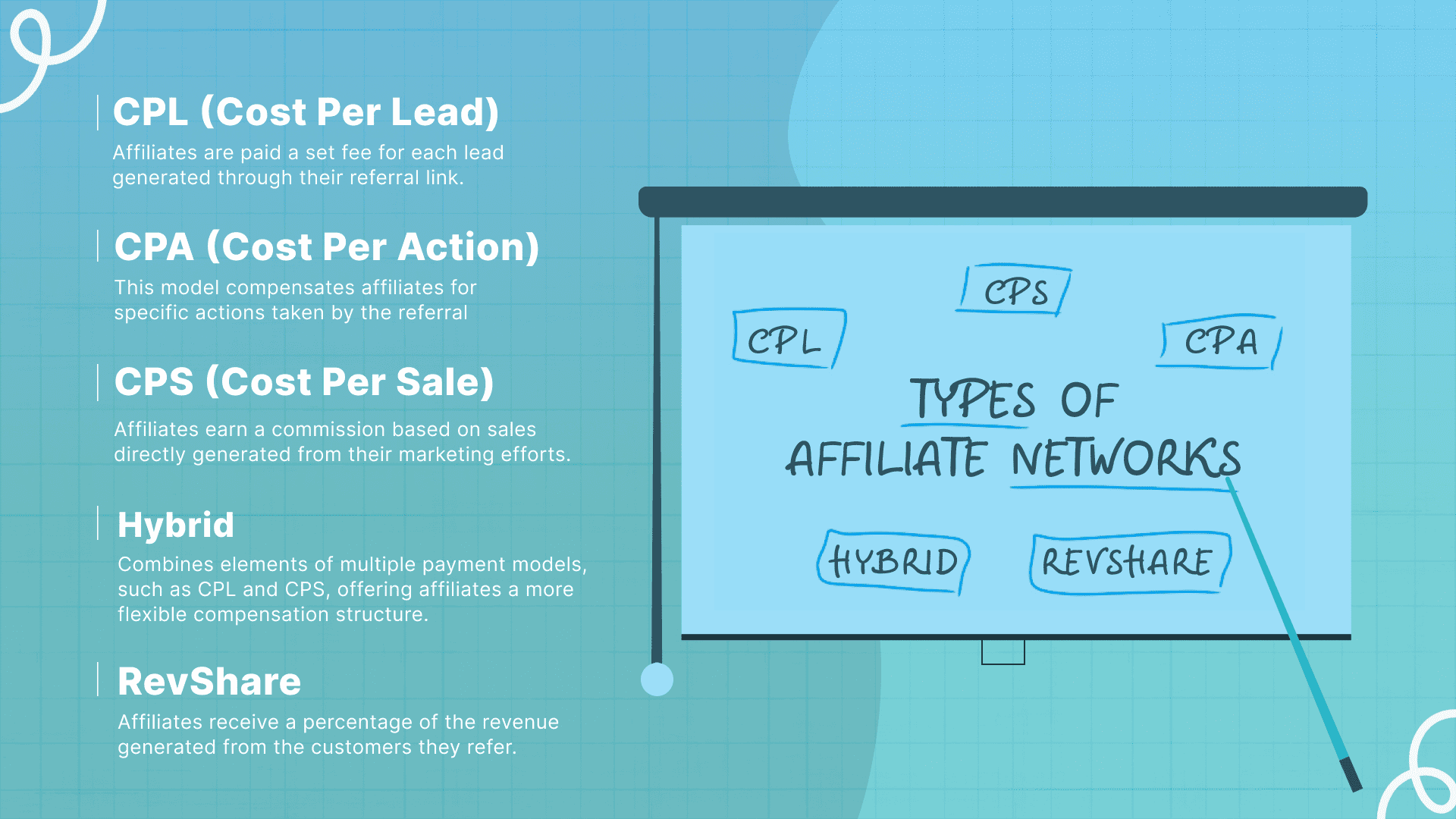
This typology is usually based on the payment models used in the network:
- CPL (Cost Per Lead)
Affiliates are paid a set fee for each lead generated through their referral link. This model is ideal for businesses focused on gathering potential customer information, such as email addresses or sign-ups, rather than making immediate sales. - CPA (Cost Per Action)
This model compensates affiliates for specific actions taken by the referral, such as a sale, download, or subscription. The action is predefined by the advertiser, making it a popular choice for driving targeted outcomes. - CPS (Cost Per Sale)
Affiliates earn a commission based on sales directly generated from their marketing efforts. This straightforward model is widely used in e-commerce affiliate marketing, with commissions often being a percentage of the sale price. - Hybrid
Combines elements of multiple payment models, such as CPL and CPS, offering affiliates a more flexible compensation structure. Affiliates might receive a smaller commission for leads in addition to a larger commission for completed sales, encouraging both lead generation and sales conversion. - RevShare (Revenue Sharing)
Affiliates receive a percentage of the revenue generated from the customers they refer, often over the lifetime of the customer’s engagement with the product or service. This model encourages affiliates to build long-term, valuable customer relationships for the advertiser.
Benefits of partnership with affiliate networks
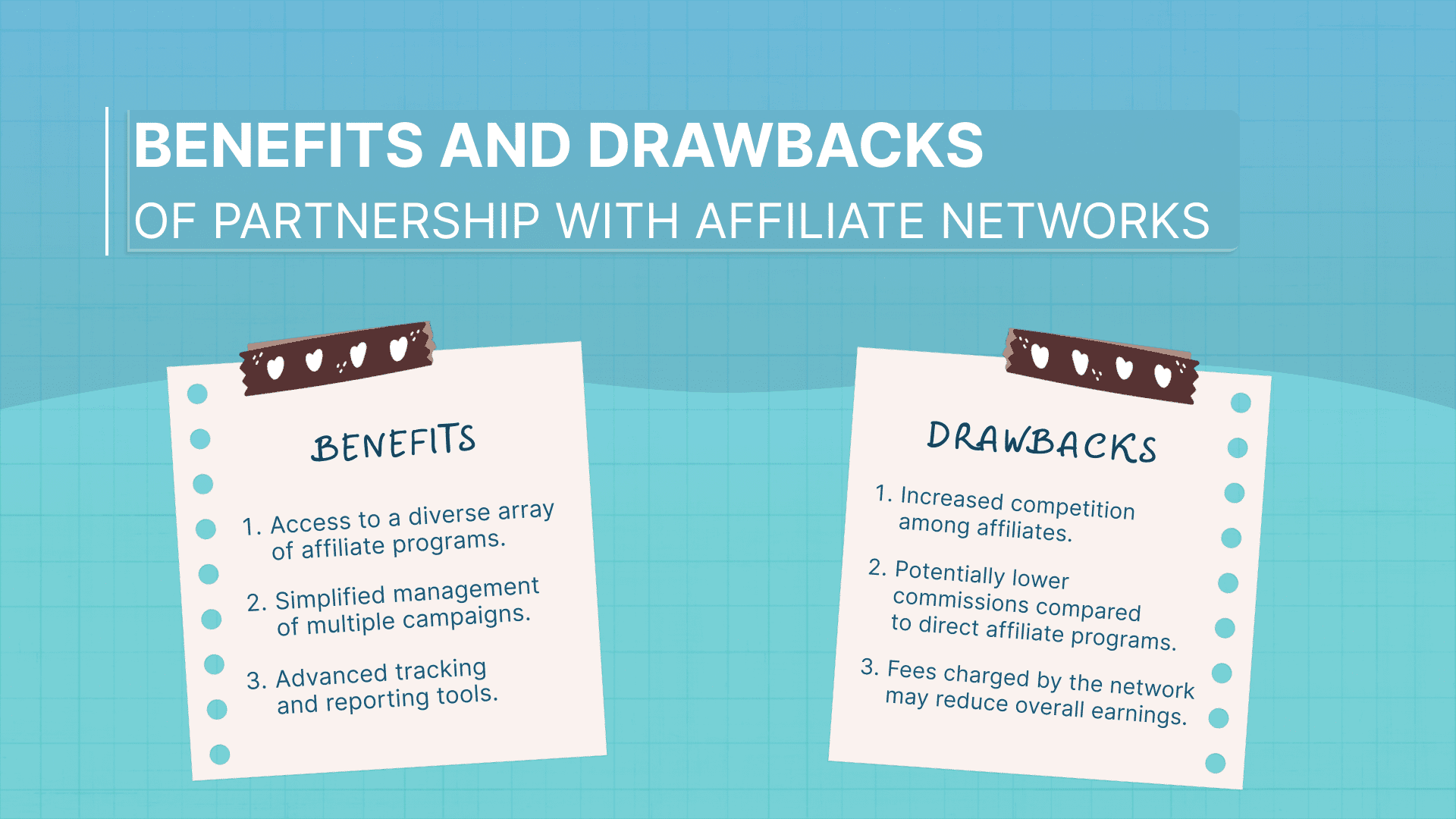
- Access to a diverse array of affiliate programs.
- Simplified management of multiple campaigns.
- Advanced tracking and reporting tools.
Drawbacks of partnership with affiliate networks
- Increased competition among affiliates.
- Potentially lower commissions compared to direct affiliate programs.
- Fees charged by the network may reduce overall earnings.
Ad network vs. affiliate network: why can they be confused?
Ad networks and affiliate networks are frequently confused due to their overlapping roles in the digital marketing environment, where both serve as intermediaries between publishers (or website owners) and advertisers (or merchants). However, they cater to different aspects of online advertising and marketing, which can blur the lines for those not intimately familiar with their distinct functions. Here are the main reasons why it sometimes seems that ad and affiliate networks are twins:
Intermediary role
Both operate as intermediaries, connecting two parties for the purpose of online advertising or marketing. Ad networks link advertisers with websites willing to display their ads, while affiliate networks connect merchants with affiliates to promote their products or services. This fundamental intermediary function can make it challenging to differentiate between the two at a glance.
Digital marketing tools
They are both considered essential tools in digital marketing strategies, often used to increase brand awareness, generate leads, or drive sales. Their role in supporting marketing objectives contributes to the confusion, as they appear to offer similar benefits from a broader perspective.
Performance-based compensation
Both networks tend to employ performance-based payment models, such as Cost Per Click (CPC) for ad networks and CPA model for affiliate networks. This similarity in monetization strategies can obscure the differences in how they operate and the specific purposes they serve.
Online advertising component
Affiliate networks, while distinct in their reliance on affiliates for marketing, still involve an element of online advertising — affiliates typically use ads to promote products or services. This overlap with the advertising realm can make it difficult for newcomers to distinguish between the direct advertising approach of ad networks and the partnership-based model of affiliate networks.
Use of digital platforms
Both types of networks leverage digital platforms, including websites, blogs, and social media, to reach their target audiences. The use of these common platforms for ad placement or promotional activities contributes to the confusion, making it seem like they operate in the same manner.
Profit maximization strategy = affiliate network + advertising network
By understanding the unique advantages of both ad networks and affiliate networks, you can craft a comprehensive digital marketing strategy that maximizes profit. Here are some tips on how to do it.
Understand their distinct roles
Yes, again.
- Ad Networks focus on selling advertising space across various media outlets to display ads, such as banners or videos, based on CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions) or CPC (Cost Per Click) models.
+
- Affiliate networks connect businesses with affiliate marketers who promote products or services to their audience on a commission basis, typically through CPA (Cost Per Action) or revenue-sharing models.
Diversify your marketing approach
- Utilize ad networks for broad exposure and brand awareness. These networks can place your ads on multiple sites and platforms, reaching diverse audiences quickly.
+
- Engage with affiliate networks to deepen your market penetration and target specific niches. Affiliates can offer personalized endorsements and reviews, driving conversions through trust and credibility.
Optimize for different stages of the sales funnel
- Use ad networks for the top of the funnel to attract a wide audience and create interest in your products or services.
+
- Implement affiliate networks as a strategy for the middle and bottom of the funnel, where targeted promotion can convert interest into sales.
Leverage data and analytics
- Analyze performance data from both networks to understand your audience better and refine your advertising and affiliate strategies.
+
- Track metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and ROI to identify which channels and partners are most effective for your business.
Foster strong relationships
- Build strong relationships with high-performing affiliates, providing them with the resources and incentives to promote your products effectively.
+
- Negotiate with ad networks for better rates or premium ad placements to maximize your visibility and reach.
Continuously test and adapt
- Experiment with different ad formats, placements, and affiliate partners to find the most effective combinations.
+
- Stay adaptable, monitoring industry trends and adjusting your strategies to leverage new technologies or platforms that can increase your profit margins.
Final thoughts
Maximizing profit in digital marketing concentrates around understanding the roles of affiliate and advertising networks. Key strategies include diversifying across both networks, aligning tactics with the sales funnel, leveraging data for optimization, building strong partnerships, and staying adaptable to changes in the digital landscape. In a nutshell, skilful navigation and strategic use of these networks are essential for achieving marketing success and optimizing online profitability.


















